Write The Formulas For Acids
vii.3: Names and Formulas of Acids
- Folio ID
- 221510
Acids
An acid tin exist defined in several ways. The almost straightforward definition is that an acrid is a molecular compound that contains one or more hydrogen atoms and produces hydrogen ions \(\left( \ce{H^+} \right)\) when dissolved in water.

This is a different type of chemical compound than the others we have seen and so far. Acids are molecular, which means that in their pure state they are individual molecules and practise not prefer the extended three-dimensional structures of ionic compounds like \(\ce{NaCl}\). However, when these molecules are dissolved in water, the chemical bond between the hydrogen cantlet and the rest of the molecule breaks, leaving a positively-charged hydrogen ion and an anion. This can be symbolized in a chemical equation:
\[\ce{HCl} \rightarrow \ce{H^+} + \ce{Cl^-}\]
Since acids produce \(\ce{H^+}\) cations upon dissolving in water, the \(\ce{H}\) of an acid is written get-go in the formula of an inorganic acid. The balance of the acid (other than the \(\ce{H}\)) is the anion afterward the acid dissolves. Organic acids are besides an of import class of compounds, only will non be discussed here.
Naming Acids
Since all acids contain hydrogen, the proper name of an acid is based on the anion that goes with it. These anions tin can either exist monatomic or polyatomic.
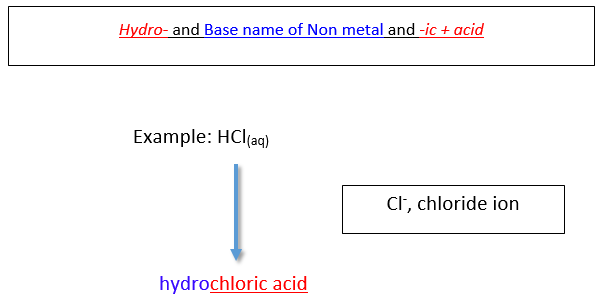
Naming Binary acids (in aqueous form)
A binary acid is an acrid that consists of hydrogen and one other element. The most common binary acids contain a halogen. The acid name begins with the prefix hydro- . followed by the base of operations name of the anion, followed past the suffix -ic .
Naming Oxyacids
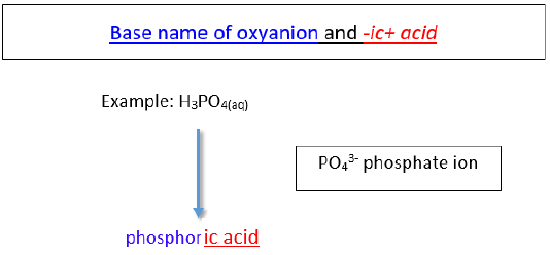
An oxyacid is an acid that consists of hydrogen, oxygen, and a 3rd chemical element. The third element is usually a nonmetal.
a. Oxyanions with -ite ending.
The name of the acid is the root of the anion followed past the suffix -ous . There is no prefix.
b. Oxyanions with -ate ending.
The name of the acrid is the root of the anion followed by the suffix -ic . There is no prefix.
Note
The base of operations proper name for sulfur containing oxyacid is sulfur- instead of simply sulf- . The same is true for a phosphorus containing oxyacid. The base name is phosphor- instead of simply phosph- .
Writing Formulas for Acids
Like other compounds that we have studied, acids are electrically neutral. Therefore, the charge of the anion part of the formula must exist exactly balanced out by the \(\ce{H^+}\) ions. Another way to call back about writing the correct formula is to use the crisscross method, shown below for sulfuric acid.
Formula: HtwoSO4
Effigy \(\PageIndex{ii}\): Crisscross arroyo to writing formula for sulfuric acid.
Summary
- Acids are molecular compounds that release hydrogen ions.
- A binary acid consists of hydrogen and 1 other element.
- Oxyacids contain hydrogen, oxygen, and one other element.
- The name of the acrid is based on the anion fastened to the hydrogen.
Contributions & Attributions
This page was synthetic from content via the post-obit contributor(s) and edited (topically or extensively) by the LibreTexts development team to meet platform manner, presentation, and quality:
-
Marisa Alviar-Agnew (Sacramento City College)
-
Henry Agnew (UC Davis)
Write The Formulas For Acids,
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Brevard_College/CHE_104%3A_Principles_of_Chemistry_II/07%3A_Acid_and_Base_Equilibria/7.03%3A_Names_and_Formulas_of_Acids
Posted by: nissenwifilbeem.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Write The Formulas For Acids"
Post a Comment