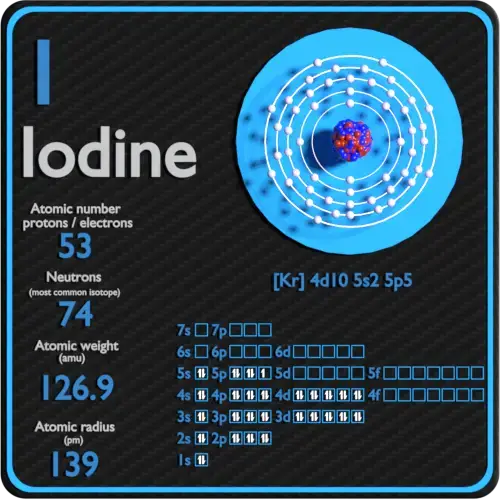
Iodine is the heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists every bit a lustrous, royal-blackness metallic solid at standard conditions that sublimes readily to form a violet gas. Iodine is the least abundant of the stable halogens, being the sixty-kickoff most abundant element. Information technology is fifty-fifty less arable than the so-called rare earths. It is the heaviest essential mineral nutrient.
Protons and Neutrons in Iodine
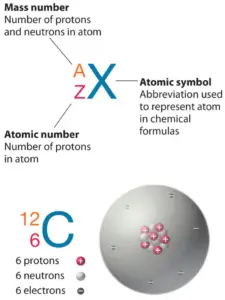 Iodine is a chemical element with diminutive number53 which ways there are 53 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The full electric accuse of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary accuse) equals to1,602 x ten-19 coulombs.
Iodine is a chemical element with diminutive number53 which ways there are 53 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The full electric accuse of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary accuse) equals to1,602 x ten-19 coulombs.
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called theneutron number of the atom and is given thesymbol North. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number:North+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known every bit theneutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
For stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes. Isotopes are nuclides that take the same diminutive number and are therefore the same element, merely differ in the number of neutrons. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Iodine are127.
Main Isotopes of Iodine
Iodine occurs in 2 natural isotopes: 127I and 129I. 129I is very slightly radioactive, decaying by beta disuse with a half-life of i.57×107 years and occurs only in traces. 127I is the most common isotope, having a natural abundance of approximately 100%.
Iodine-127 is composed of 53 protons, 74 neutrons, and 53 electrons.
Iodine-129 is composed of 53 protons, 76 neutrons, and 53 electrons.
Electrons and Electron Configuration
The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral cantlet is the aforementioned as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Iodine is 53. Each electron is influenced past the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom.
Since the number of electrons and their organization are responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, theatomic number identifies the various chemical elements. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element's electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the principal cistron in determining its chemical bonding beliefs. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
Electron configuration ofIodineis[Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p5.
Possible oxidation states are+ane,five,vii/-1.
Almost Common Application of Iodine
Mutual application of iodine is the tincture of iodine, which is an antiseptic. It is commonly 2 to 7% elemental iodine, along with potassium iodide or sodium iodide, dissolved in a mixture of ethanol and water. Tincture solutions are characterized by the presence of alcohol.
Nearly Protons
 A proton is one of the subatomic particles that brand upwards matter. In the universe, protons are arable, making upwardlyalmost half of all visible affair. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to ane.67262 × ten−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron but nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean square radius of about 0.87 × ten−15 m, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
A proton is one of the subatomic particles that brand upwards matter. In the universe, protons are arable, making upwardlyalmost half of all visible affair. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to ane.67262 × ten−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron but nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean square radius of about 0.87 × ten−15 m, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
The protons be in the nuclei of typical atoms, along with their neutral counterparts, the neutrons. Neutrons and protons, commonly callednucleons, are spring together in the atomic nucleus, where they account for 99.ix percent of the atom's mass. Research in high-free energy particle physics in the 20th century revealed that neither the neutron nor the protonis not the smallest building block of matter.
About Neutrons
A neutron is one of the subatomic particles that brand upward affair. In the universe, neutrons are abundant, making upmore one-half of all visible affair. It hasno electric charge and a balance mass equal to one.67493 × x−27 kg—marginally greater than that of the proton simply nearly 1839 times greater than that of the electron. The neutron has a mean square radius of most 0.8×10−15 thousand, or 0.8 fm, and information technology is a spin-½ fermion.
Atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons, which attract each other throughthe nuclear forcefulness, while protons repel each other viathe electric force due to their positive charge. These two forces compete, leading to various stability of nuclei. There are only sure combinations of neutrons and protons, which formsstable nuclei.
Neutrons stabilize the nucleus, because they concenter each other and protons , which helps offset the electric repulsion between protons. As a result, as the number of protons increases,an increasing ratio of neutrons to protons is needed to form a stable nucleus. If at that place are too many or also few neutrons for a given number of protons, the resulting nucleus is non stable and it undergoes radioactive decay.Unstable isotopesdecay through various radioactive decay pathways, most commonly alpha decay, beta decay, or electron capture. Many other rare types of decay, such equally spontaneous fission or neutron emission are known. Information technology should exist noted that all of these decay pathways may be accompanied bythe subsequent emission of gamma radiation. Pure blastoff or beta decays are very rare.
About Electrons and Electron Configuration
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Knowledge of theelectron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic tabular array of elements.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Thechemical properties of the atom are adamant past the number of protons, in fact, by number andorganisation of electrons. Theconfiguration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element's electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the master cistron in determining its chemic bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing diminutive number Z.
Information technology is thePauli exclusion principle that requires the electrons in an cantlet to occupy dissimilar energy levels instead of them all condensing in the ground state. The ordering of the electrons in the footing land of multielectron atoms, starts with the lowest energy state (basis state) and moves progressively from there upwards the energy scale until each of the atom's electrons has been assigned a unique set of quantum numbers. This fact has central implications for the building upward of the periodic table of elements.
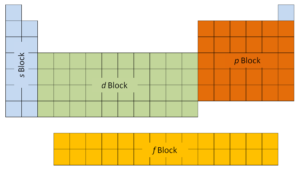 The commencement two columns on the left side of the periodic tabular array are where thes subshells are beingness occupied. Because of this, the commencement two rows of the periodic tabular array are labeled thesouthward block. Similarly, thep cakeare the correct-most six columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic tabular array, while thef cakeis the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the main torso of the periodic table. It could exist office of the main torso, only then the periodic tabular array would be rather long and cumbersome.
The commencement two columns on the left side of the periodic tabular array are where thes subshells are beingness occupied. Because of this, the commencement two rows of the periodic tabular array are labeled thesouthward block. Similarly, thep cakeare the correct-most six columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic tabular array, while thef cakeis the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the main torso of the periodic table. It could exist office of the main torso, only then the periodic tabular array would be rather long and cumbersome.
For atoms with many electrons, this notation can get lengthy so an abbreviated annotation is used. The electron configuration can be visualized as the cadre electrons, equivalent to thenoble gas of the preceding period, and the valence electrons (e.g. [Xe] 6s2 for barium).
Oxidation States
Oxidation states are typically represented by integers which may be positive, nil, or negative. Most elements have more than than one possible oxidation land. For example, carbon has ix possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +iv.
The current IUPAC Gold Book definition of oxidation land is:
"Oxidation state of an atom is the charge of this atom after ionic approximation of its heteronuclear bonds…"
and the term oxidation number is about synonymous. An element that is not combined with any other dissimilar elements has an oxidation country of 0. Oxidation state 0 occurs for all elements – it is but the element in its elemental form. An atom of an element in a compound will have a positive oxidation state if it has had electrons removed. Similarly, calculation electrons results in a negative oxidation land. We take too distinguish between the possible and common oxidation states of every element. For instance, silicon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −four to +4, but only -iv, 0 and +iv are common oxidation states.
Summary
| Element | Iodine |
| Number of protons | 53 |
| Number of neutrons (typical isotopes) | 127 |
| Number of electrons | 53 |
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p5 |
| Oxidation states | +1,5,7/-1 |

Source: www.luciteria.com
Other properties of Iodine

 Iodine is a chemical element with diminutive number53 which ways there are 53 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The full electric accuse of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary accuse) equals to1,602 x ten-19 coulombs.
Iodine is a chemical element with diminutive number53 which ways there are 53 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The full electric accuse of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary accuse) equals to1,602 x ten-19 coulombs.

 A proton is one of the subatomic particles that brand upwards matter. In the universe, protons are arable, making upwardlyalmost half of all visible affair. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to ane.67262 × ten−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron but nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean square radius of about 0.87 × ten−15 m, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
A proton is one of the subatomic particles that brand upwards matter. In the universe, protons are arable, making upwardlyalmost half of all visible affair. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to ane.67262 × ten−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron but nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean square radius of about 0.87 × ten−15 m, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion. The commencement two columns on the left side of the periodic tabular array are where thes subshells are beingness occupied. Because of this, the commencement two rows of the periodic tabular array are labeled thesouthward block. Similarly, thep cakeare the correct-most six columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic tabular array, while thef cakeis the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the main torso of the periodic table. It could exist office of the main torso, only then the periodic tabular array would be rather long and cumbersome.
The commencement two columns on the left side of the periodic tabular array are where thes subshells are beingness occupied. Because of this, the commencement two rows of the periodic tabular array are labeled thesouthward block. Similarly, thep cakeare the correct-most six columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic tabular array, while thef cakeis the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the main torso of the periodic table. It could exist office of the main torso, only then the periodic tabular array would be rather long and cumbersome.
0 Response to "Number Of Neutrons Of Iodine"
Post a Comment